Please watch video above for detailed info:
Hi Guys,
Just a short blog to explain what I mean by employing the “Down Down Up” guitar picking technique.
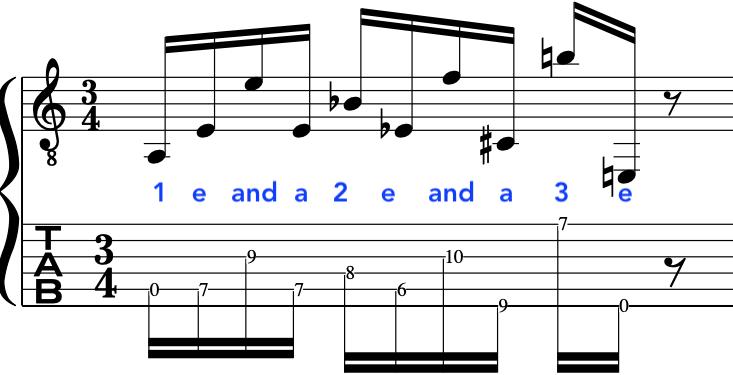
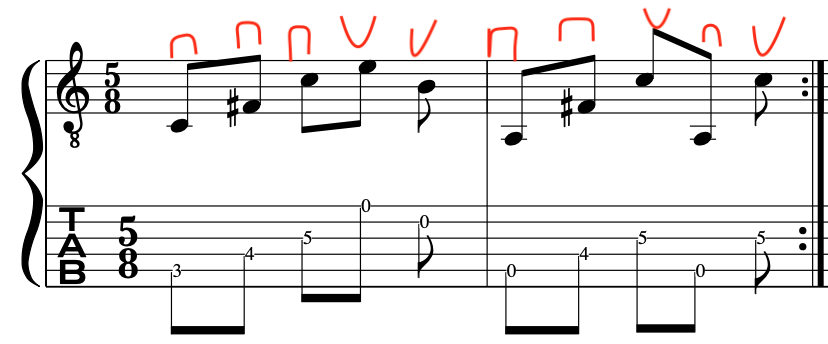
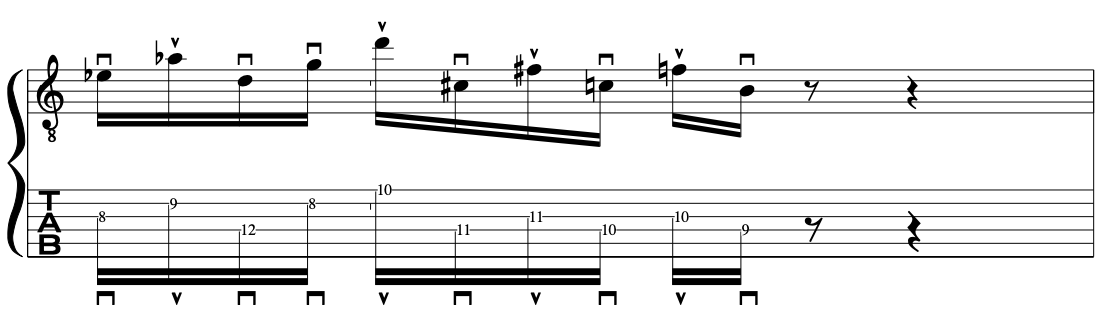
If we look at the patten below we can see the “Down Down Up” Picking pattern:

This is a very useful picking pattern/device that will hold you in good stead: But the key is to employ it sparingly.
Why is this?
This is because sometimes the rhythms we see and sometimes feel can be different than our natural inclinations when picking/plucking the strings.
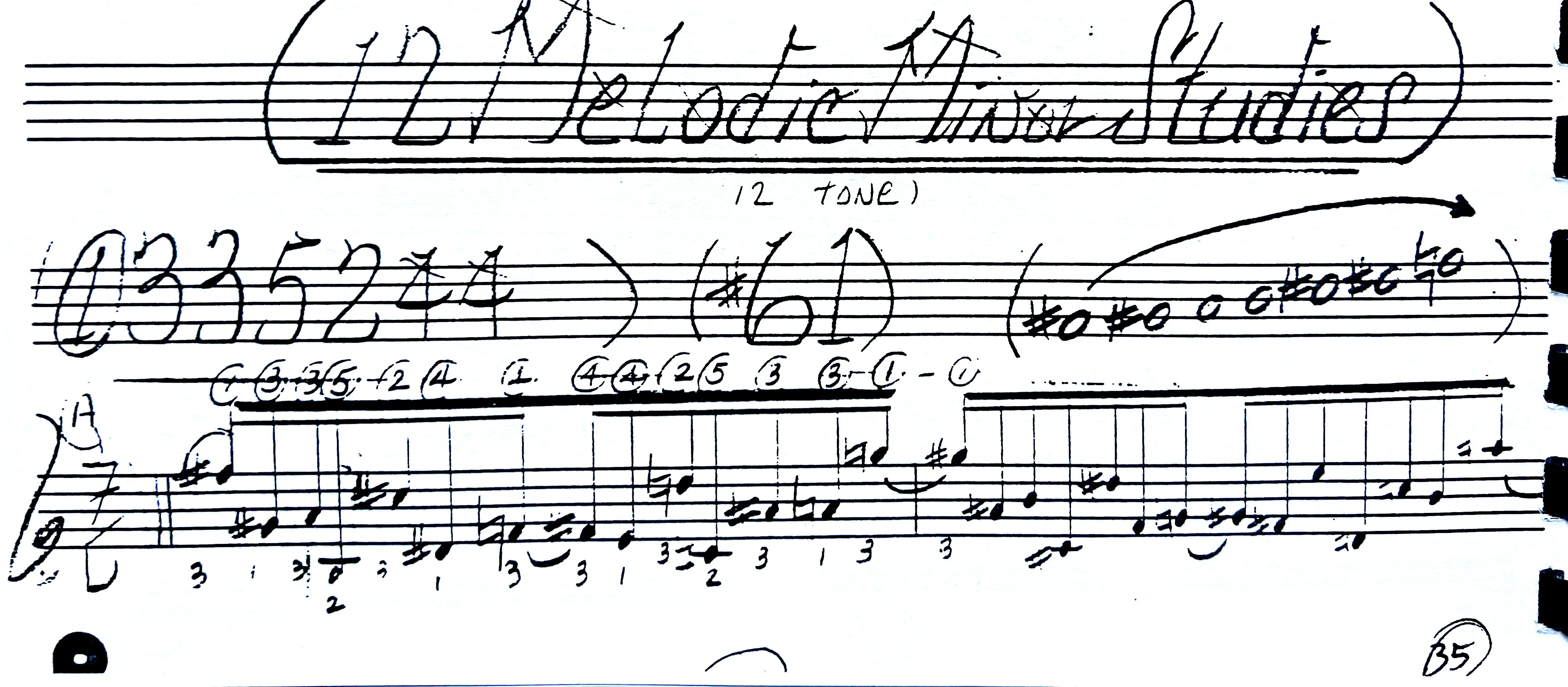
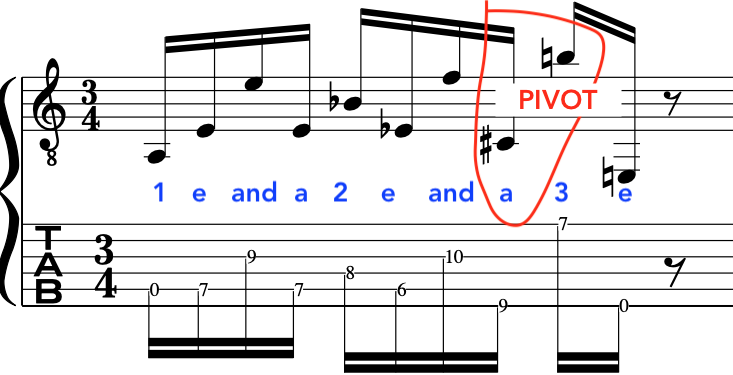
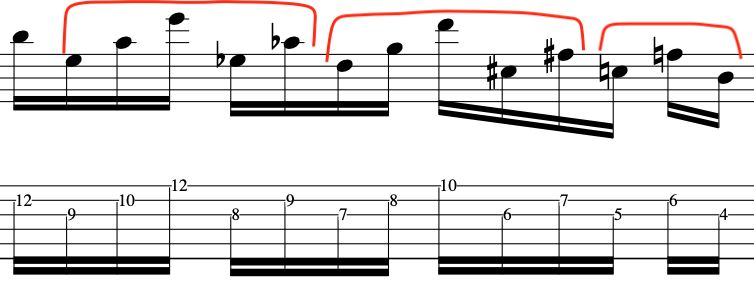
So, if we look below we will see that the picking hand/subconcious wants to pluck a group of 5 notes and 3 notes to make up the 4 and 4 groups of 16th notes.
This is because of the “Crossing” of the strings, the order of the notes or the way the actual groups of notes on the guitar fingerboard work out:
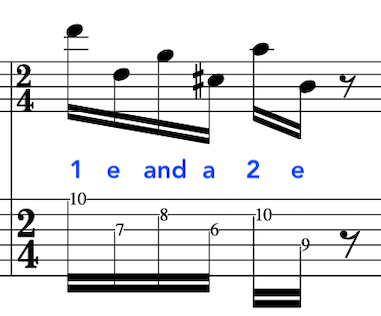
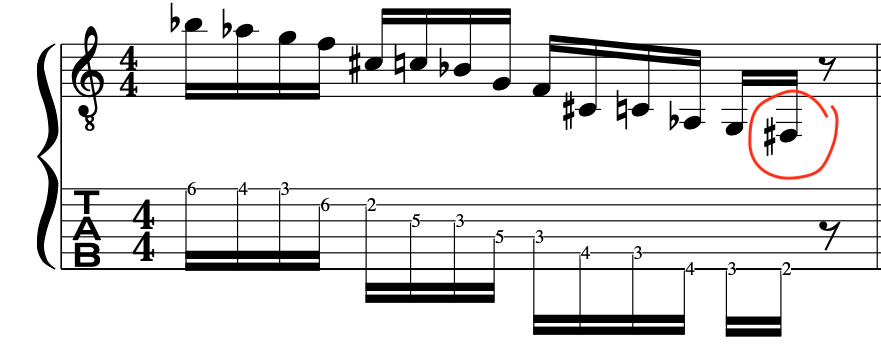
EXAMPLE:
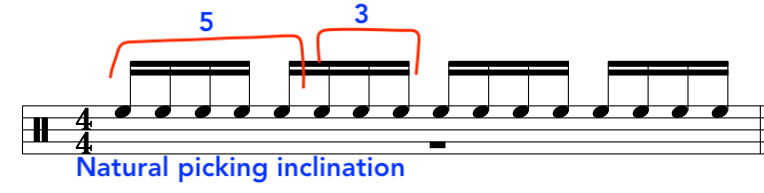
OR:
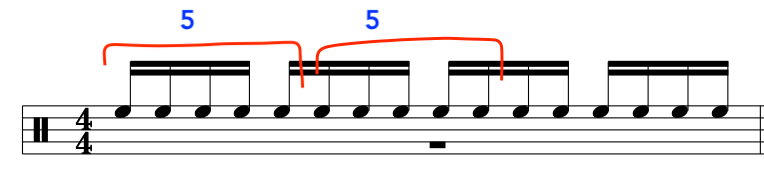
Notation Example:
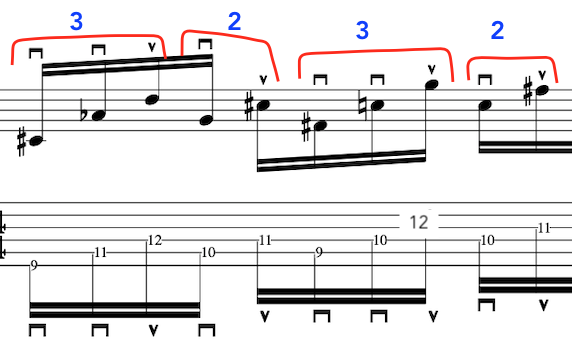
PICKING STROKES:
The other reason to put this “Down Down Up” into what would otherwise be an alternate picking pattern is because:
“Sometimes where you have a down stroke you may want an upstroke to complete the phrase”.
This can be because of one note that has to be played on a down or upstroke specifically otherwise the whole passage is awkward to play. So, to execute “Down Down Up” for that one part makes sense.
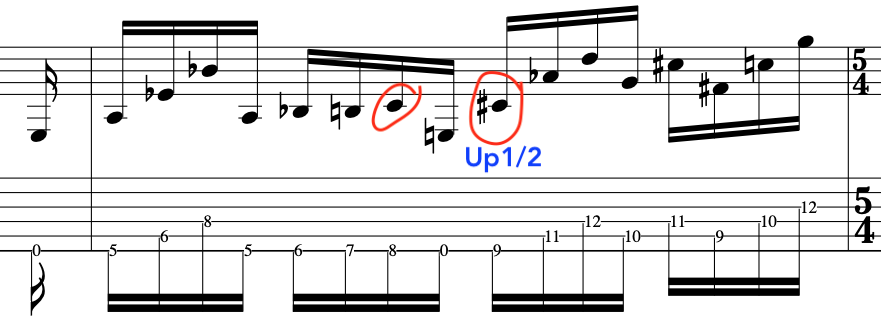
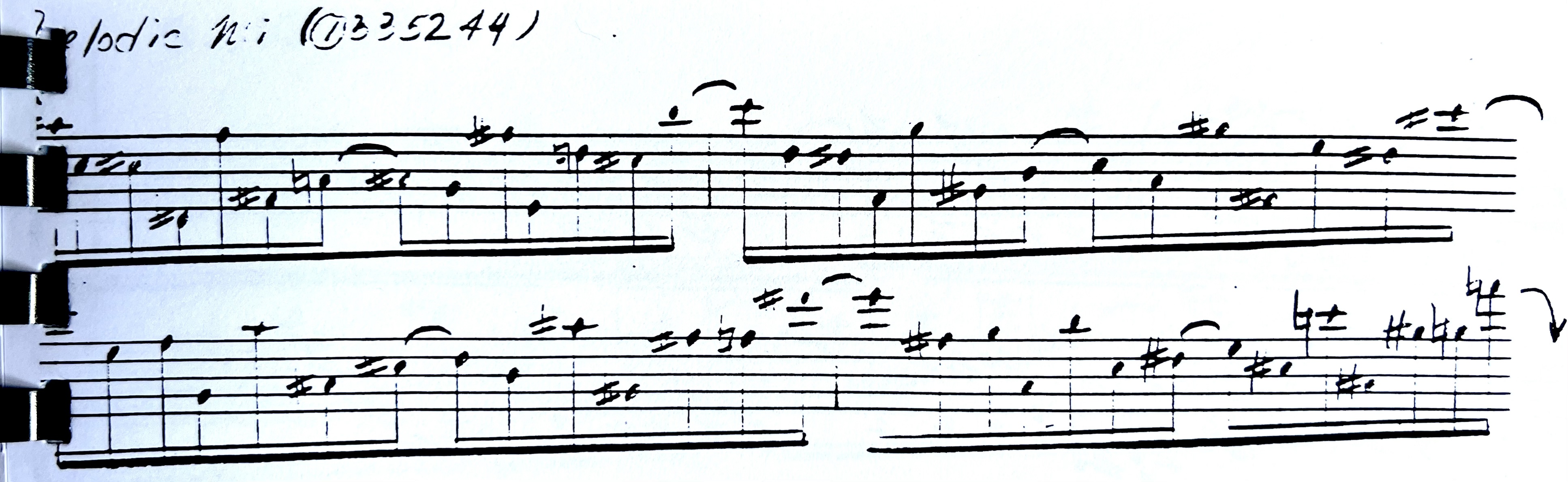
FULL EXERCISE:
Below, is the full exercise that deliberately mixes up “Down Down Up” and “Down up” Alternate Picking”. It’s only an exercise [Larks Tongues in Aspic III Style] but, hopefully it gets the point across.
Exercise:
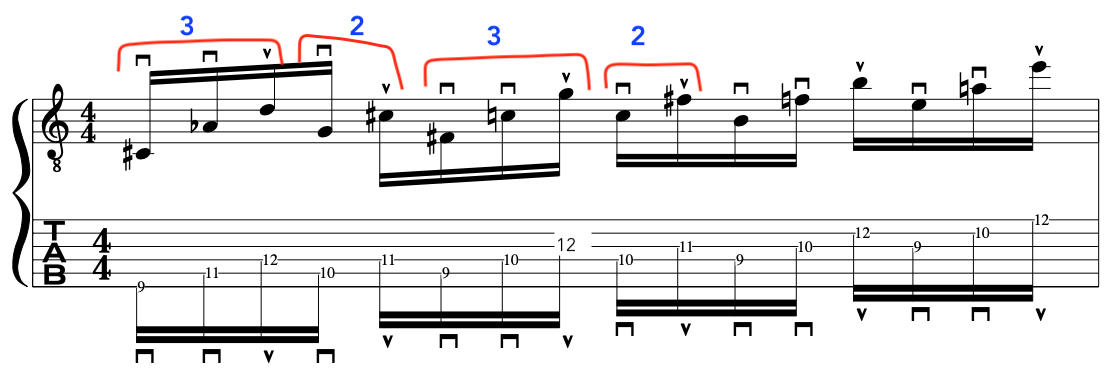
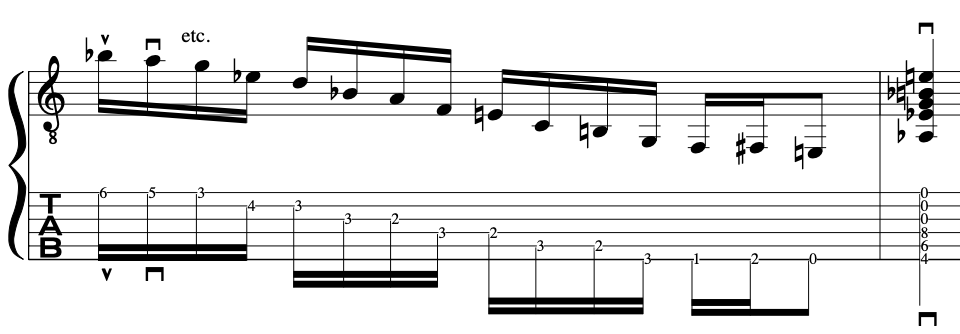
Conclusion:
This technique can also be found in Al Di Meola’s REH video from the 1980’s. Al di Meola employs this for chordal/Arpggeio Picking, [as does Fripp sometimes].
Again, if used sparingly this right hand picking pattern/technique is absolutely essential for this type of art/creative style guitar music.
Lastly, picking one note per string is way more difficult and precise than plucking standard 3 notes per string as there’s so much string crossing going on.
FREE PDF DOWNLOAD:
If this lesson was of use to you, then please SUBSCRIBE to us on YOUTUBE in the link below, Thanks!