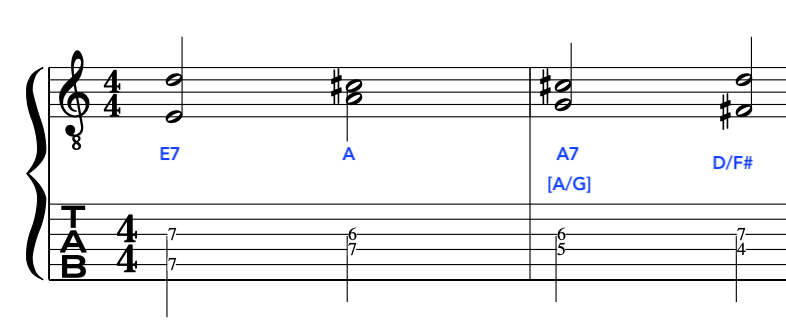
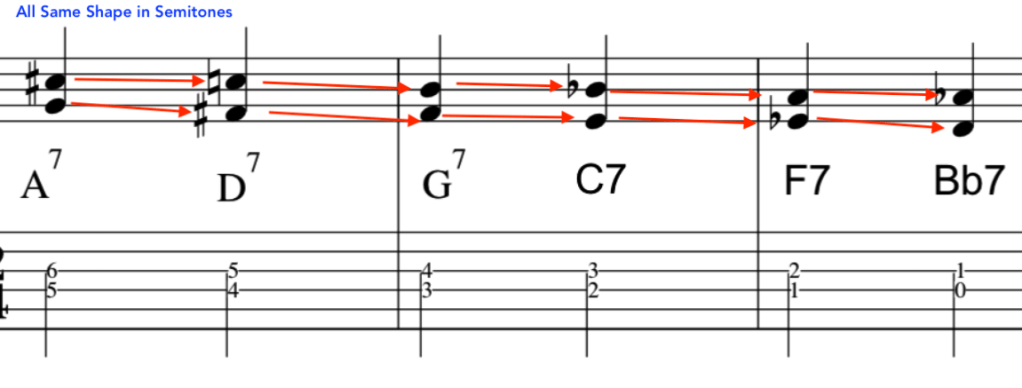
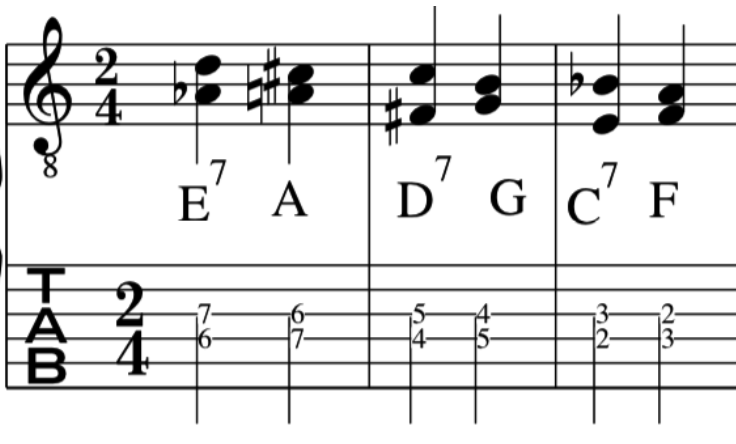
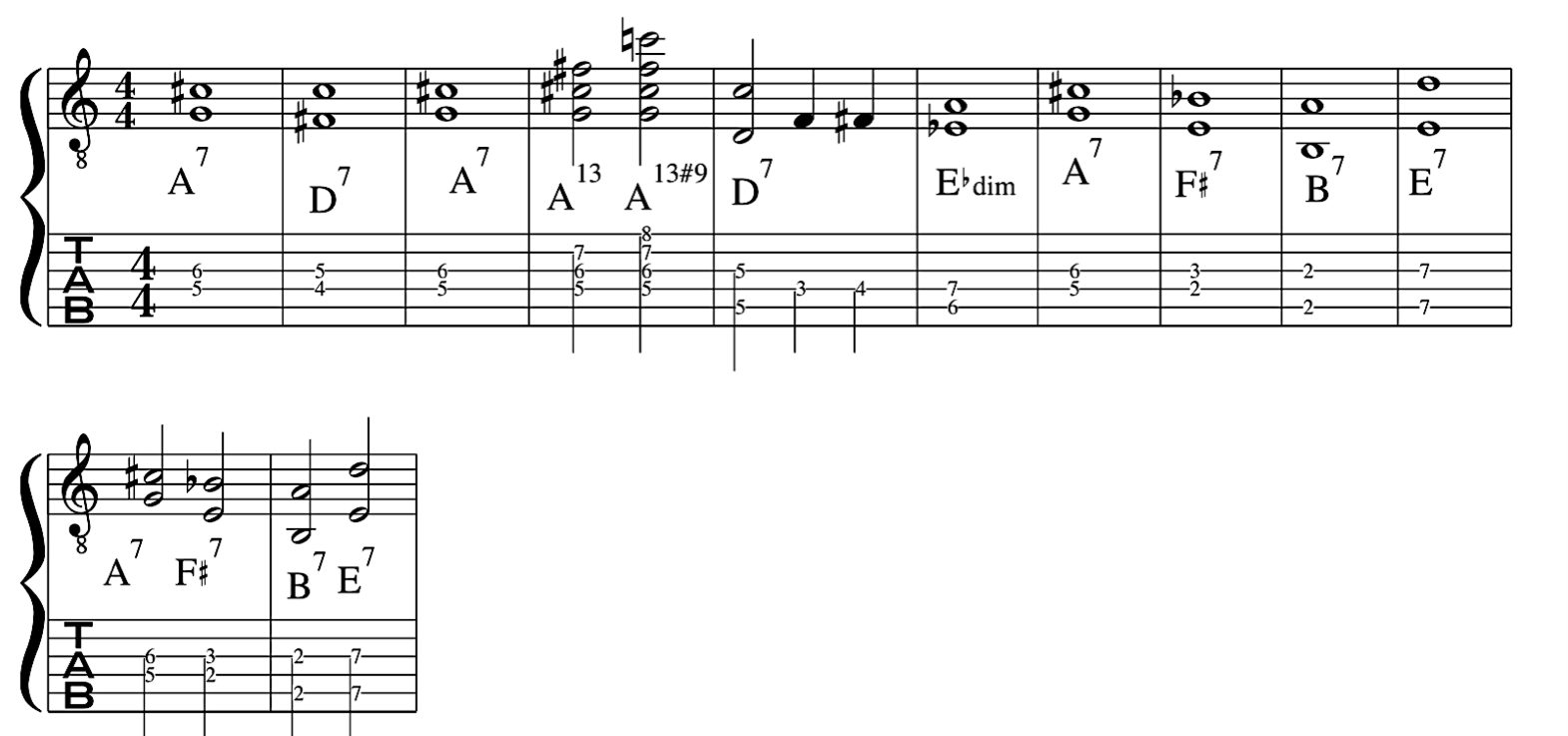
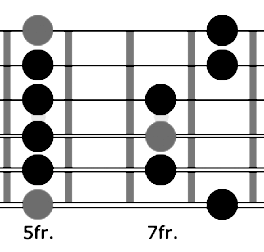
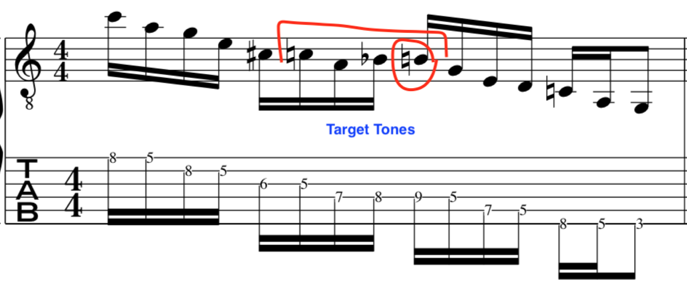
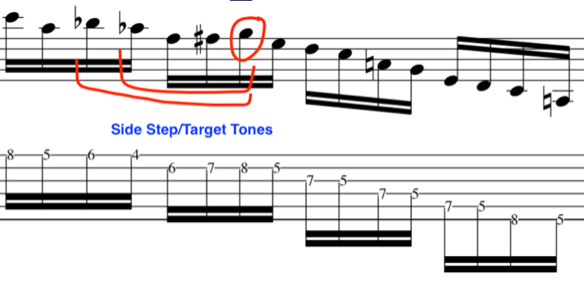
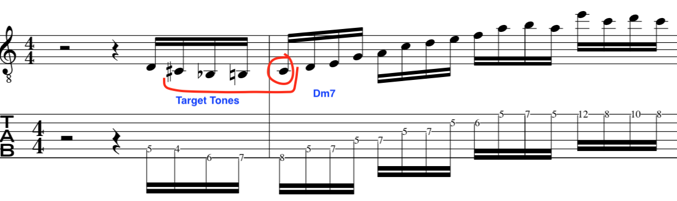
Please watch video above for detailed info:
Hi Guys,
Today, a quick look at building interesting, creative, melodic lines by pairing simple triads together.
PART 1:
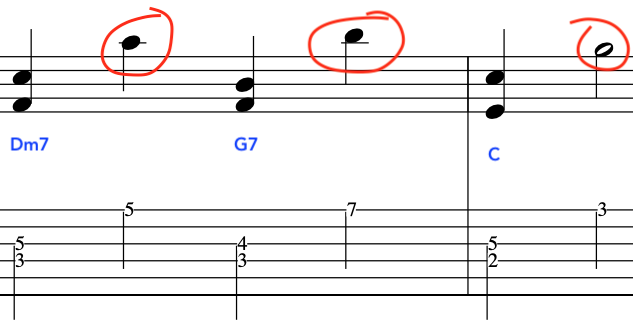
To begin with, let’s join the triads of F and G [back to F] together
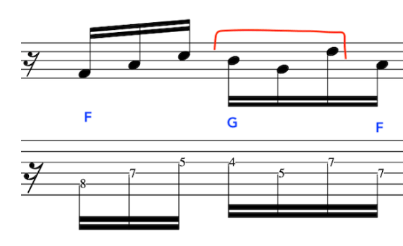
We will now, extend the line further by employing the same two triads once again,
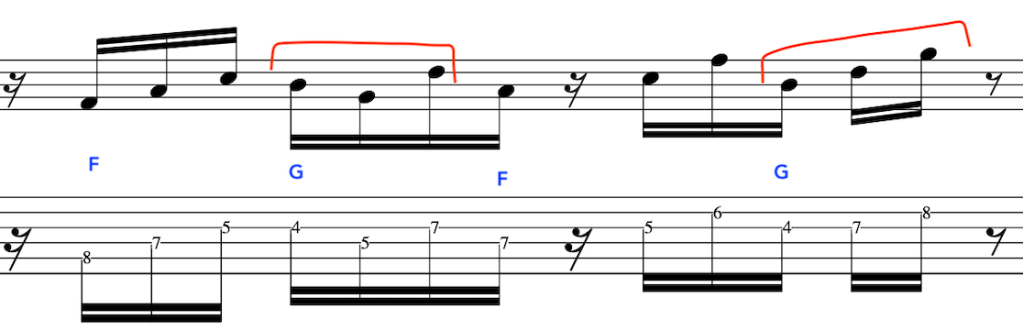
At this point we will end the phrase and create a cadence with our two triads,
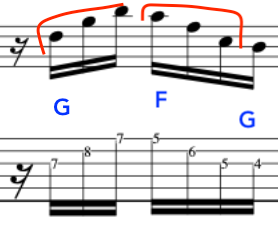
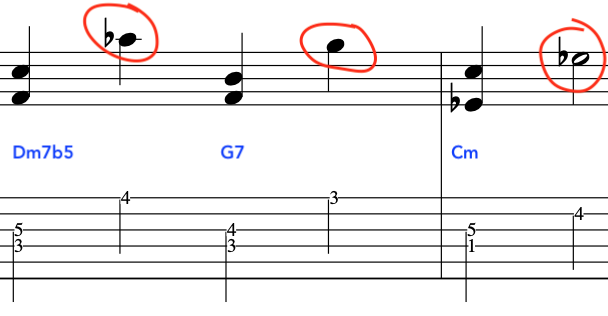
We will now shape a new line and ascend with the triads of F G and C
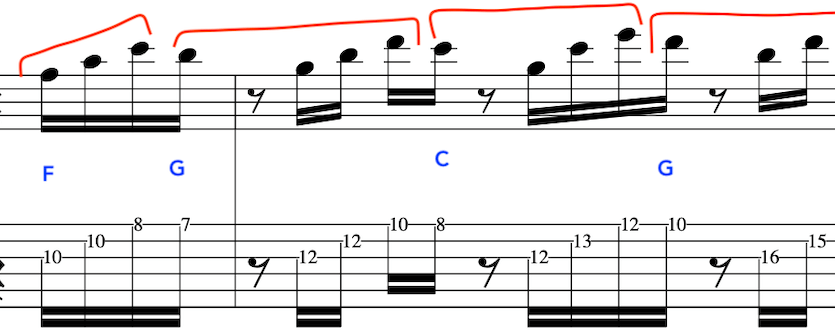
At this point the triad pairs have started to become formulaic
So, we will add some colour.
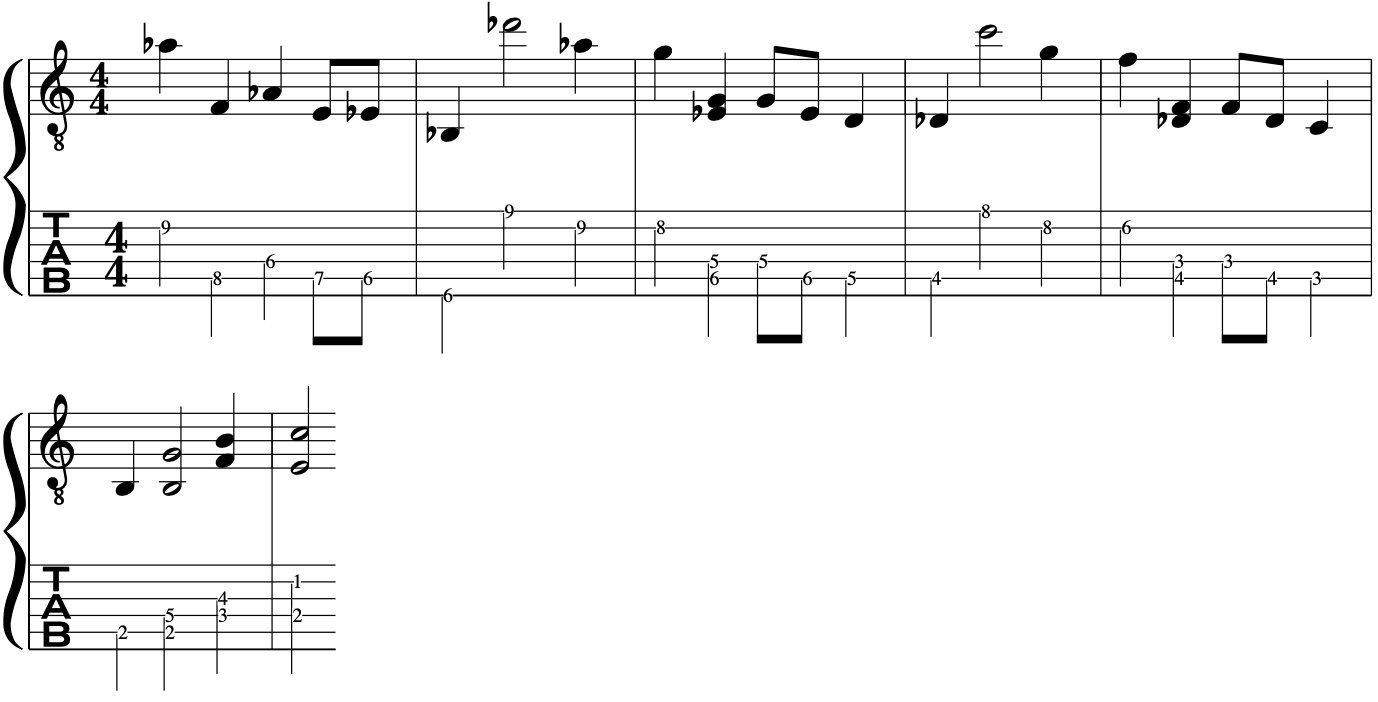
To achieve this, we will now go in the opposite direction and descend with a classic Pat Martino lick
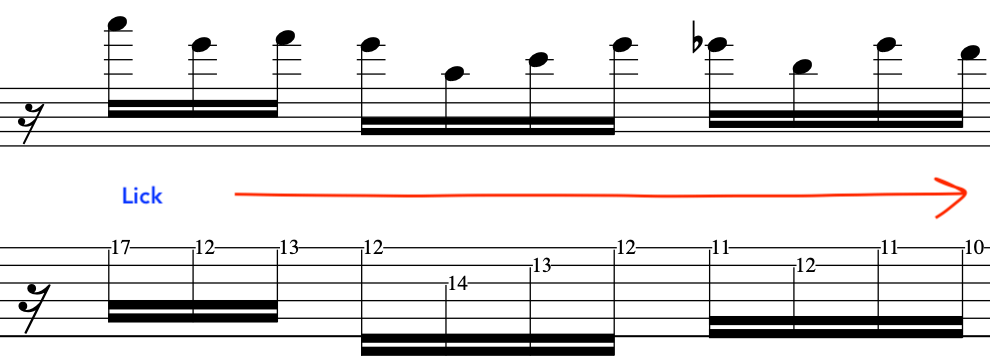
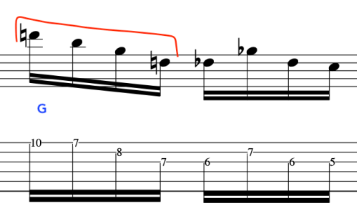
This leads us in nicely to exploit some chromatic set ups with target tones

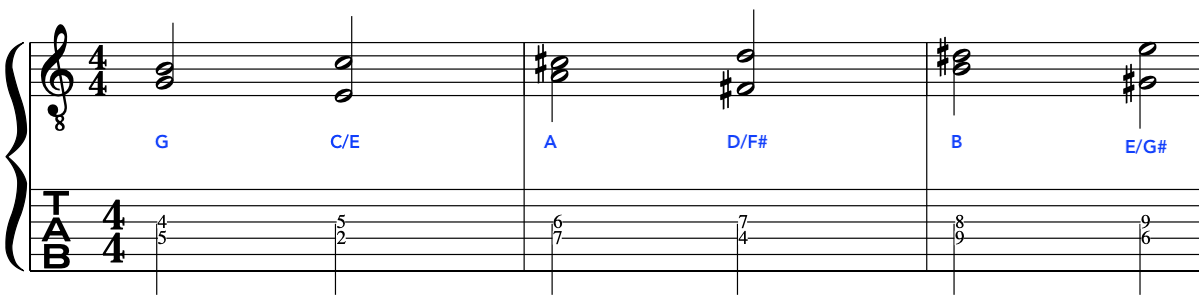
From this, we can bring in our G Major triad/arpeggio to give a wider intervallic sound to give a sense of distance from our chromatic notes.
Finally, to complete the lick we will employ some basic scale movement with chromatic fragments for the A7 chord.
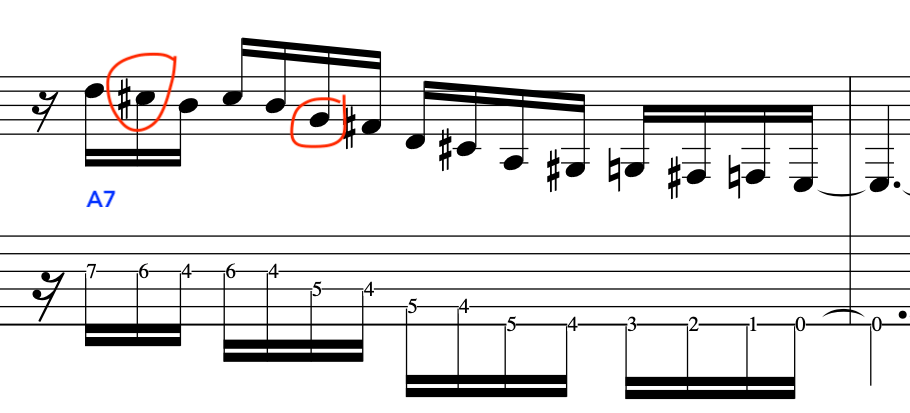
IN CONCLUSION:
Although, this was a long phrase It acts as a useful example to hear and see how natural it is to build off of triad pairs for the improvised line.
These triad pairs also create a really nice melodic and fluid way to start a phrase.
Lastly, due to the way triad pairs are offset rhythmically, the improvised line generally possesses a more composed and polished sound.
FREE PDF DOWNLOAD:
If this blog lesson was of use to you then please SUBSCRIBE to us on YOUTUBE below, Thanks!