Please watch video above for detailed info:
Hi Guys,
Today, a few alternate picking guitar exercises.
These differ slightly as they incorporate alternate picking to chord and back to alternate picking technique.
Adding a chord [or chords] can throw some players off when alternate picking, so these exercises can be really helpful.
All of these little exercises are around the 140 bpm metronome marking.
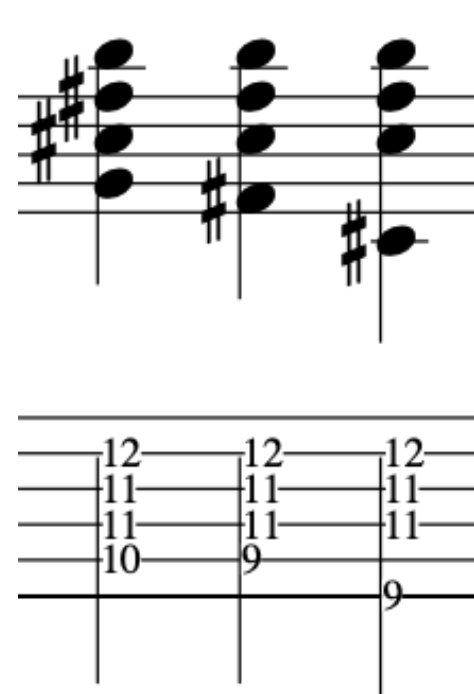
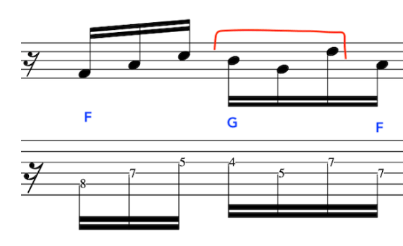
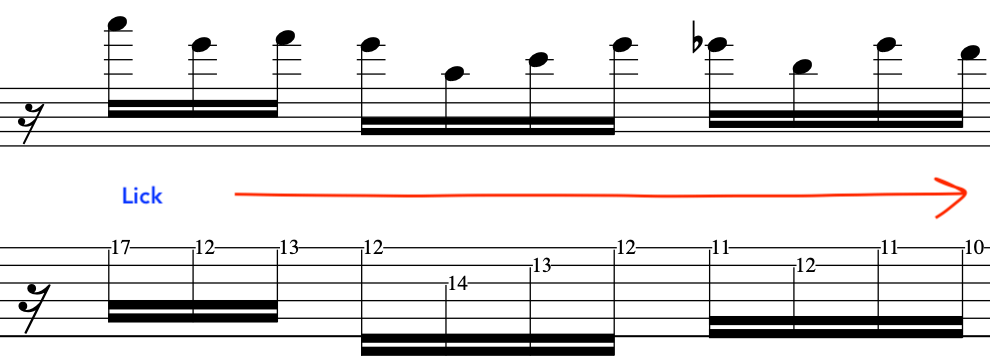
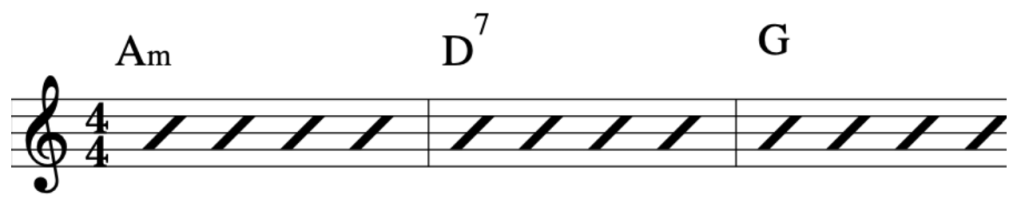
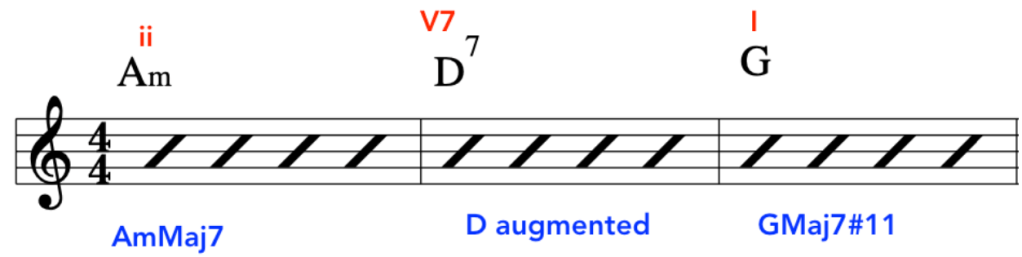
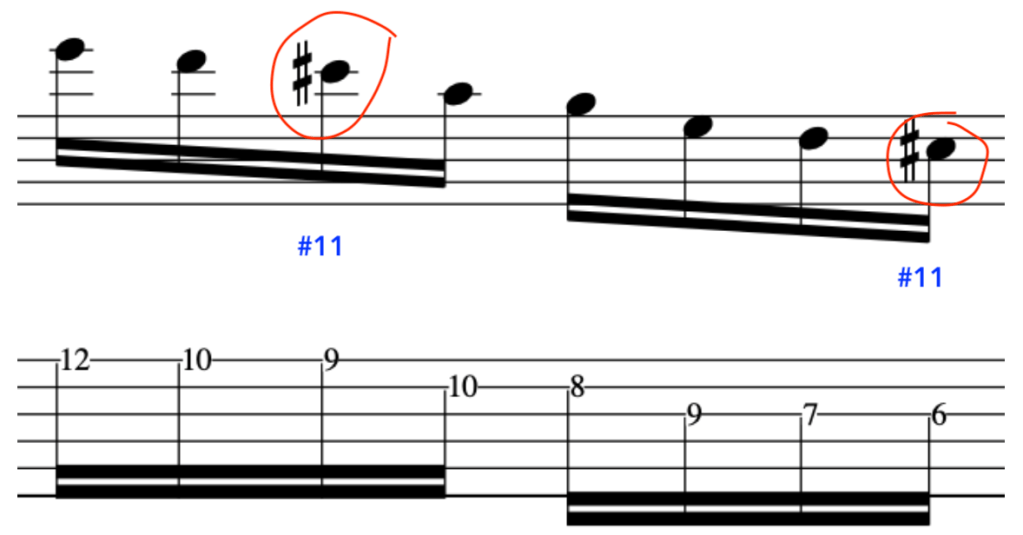
EXERCISE 1:
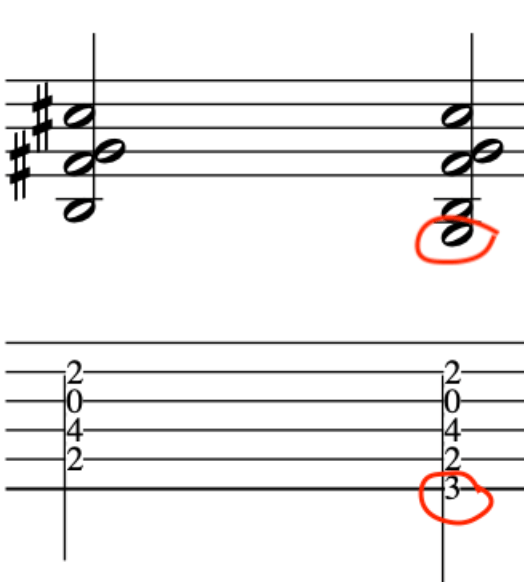
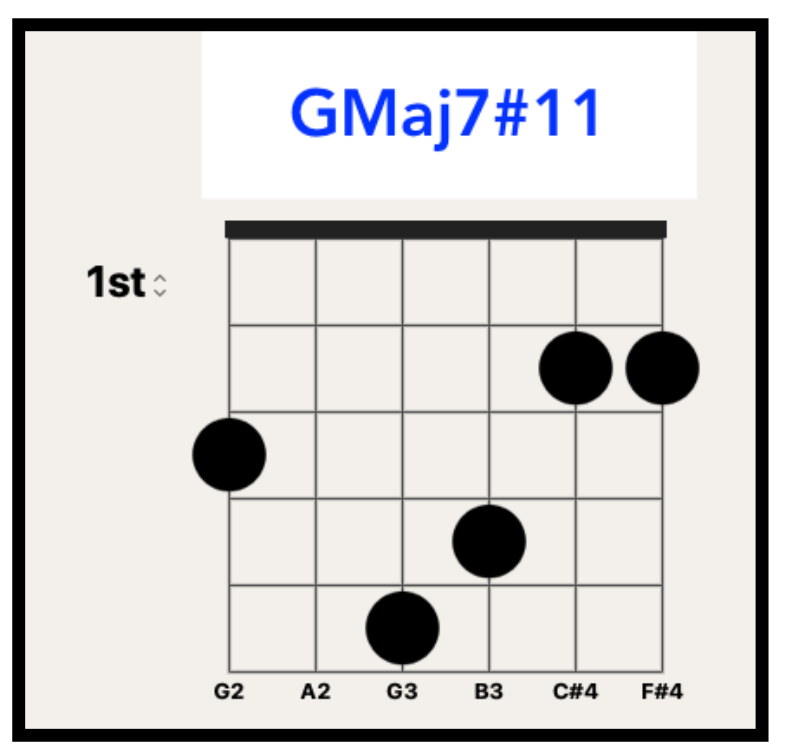
In this primer exercise we will have two sets of 16th notes that then accent a D quartal chord.
This exercise starts on a Downstroke and accents the 3rd note in each 4 note grouping.

By accenting these pitches it will make picking the exercise much smoother, due to the the last 2 notes in each 4 note grouping being prepared for and hence plucked in a deliberate fashion.
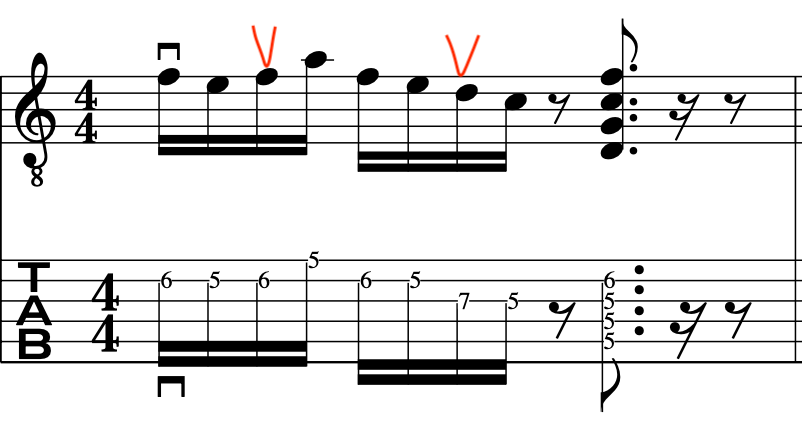
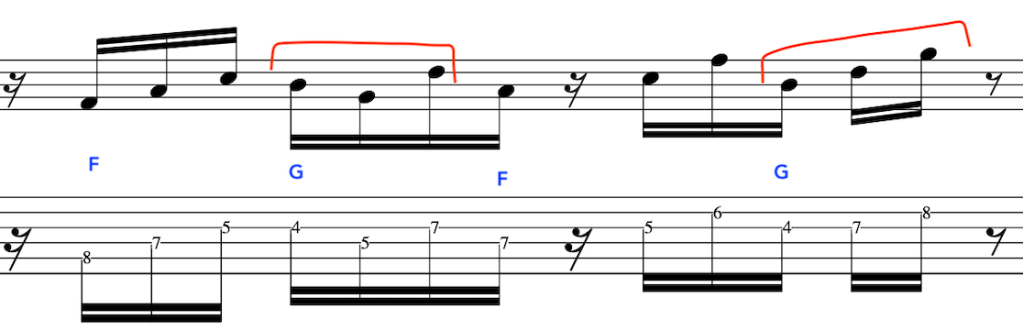
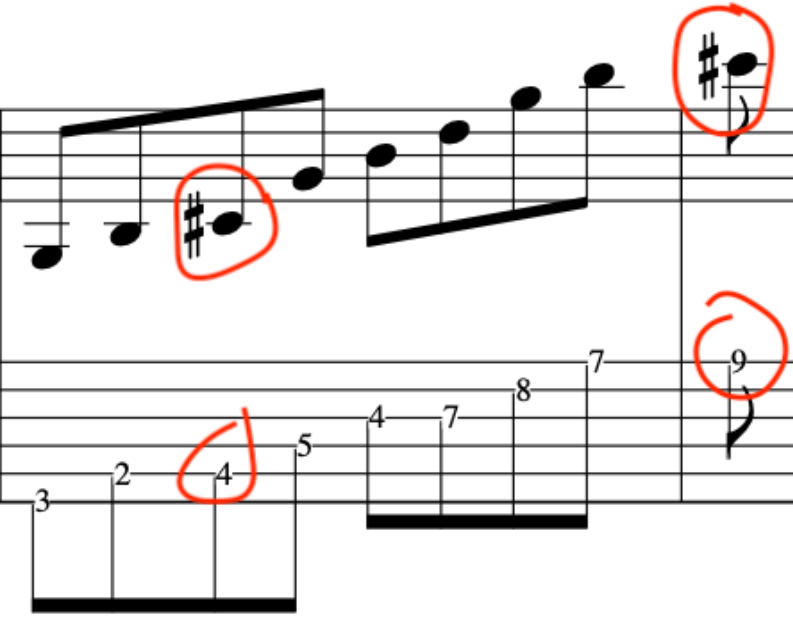
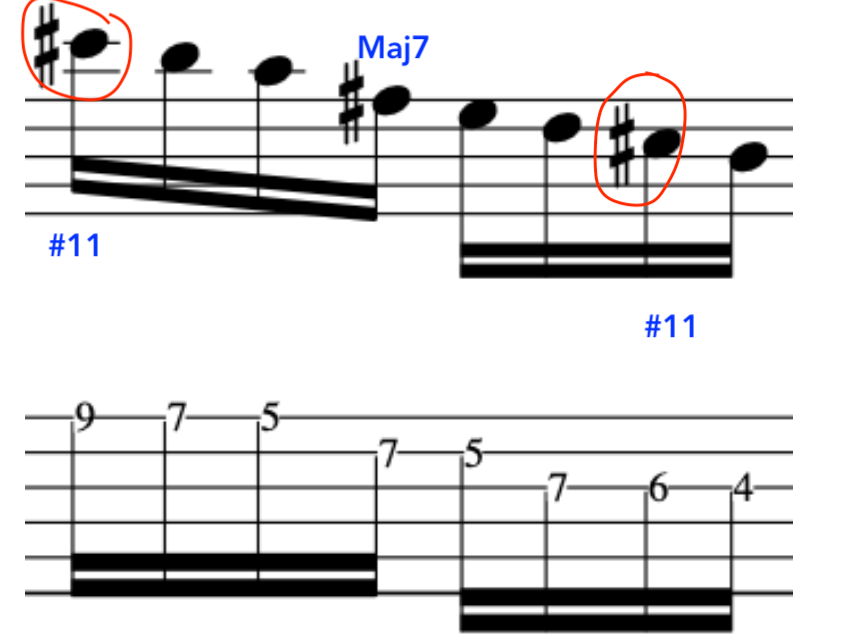
EXERCISE 2:
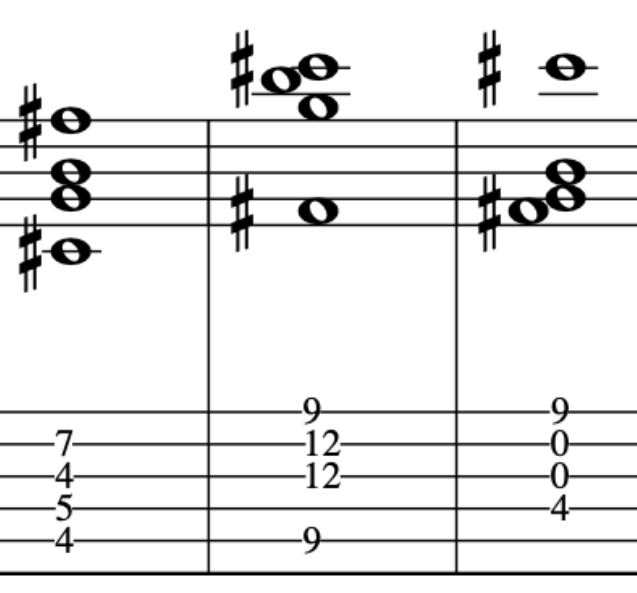
This time we will extend the previous exercise, but, start in the bar on the 2nd semiquaver.
Again, these simple concepts will affect how you pick. So, this is set as if it is for a riff or hook that is doubled up with another instrument, hence, creating a much more compositional approach.

Here is the Full Exercise:
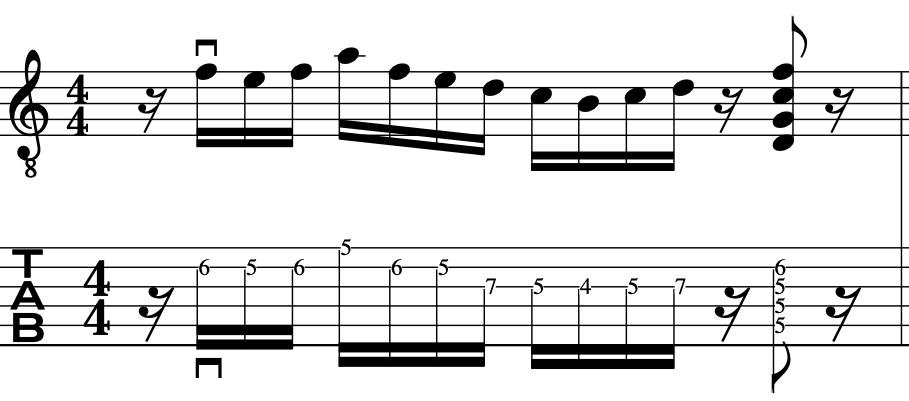
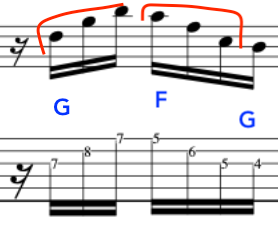
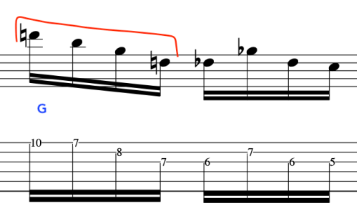
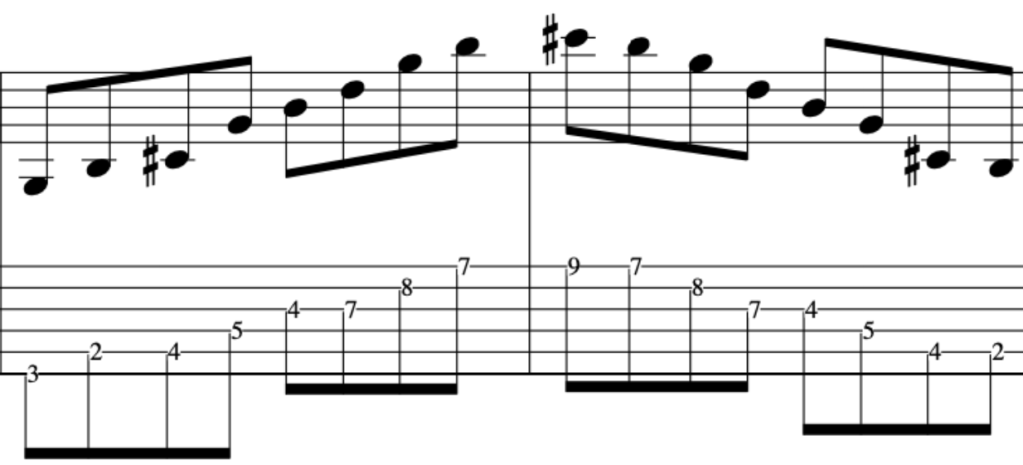
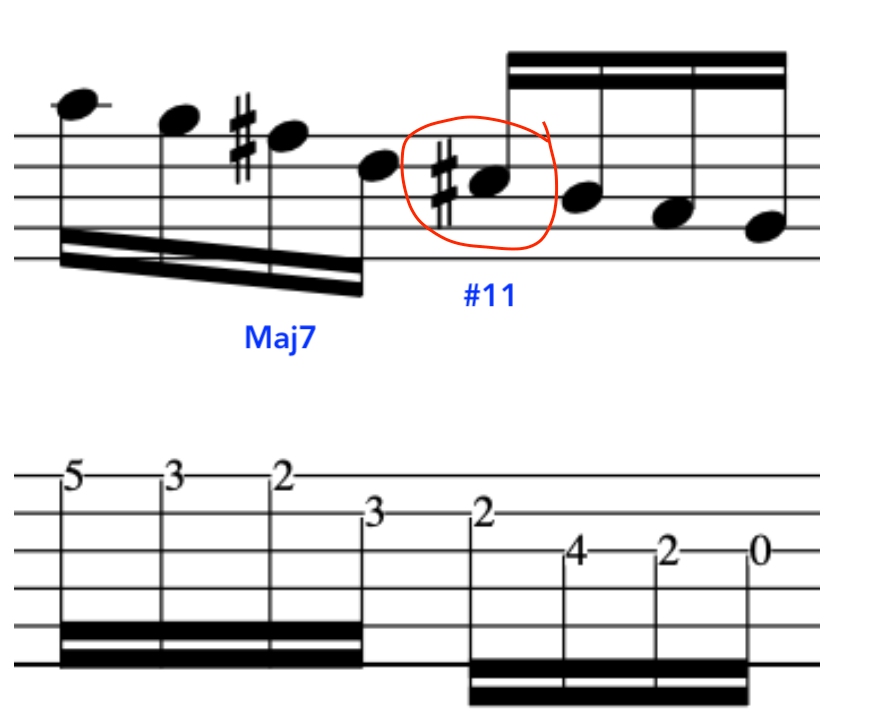
EXERCISE 3:
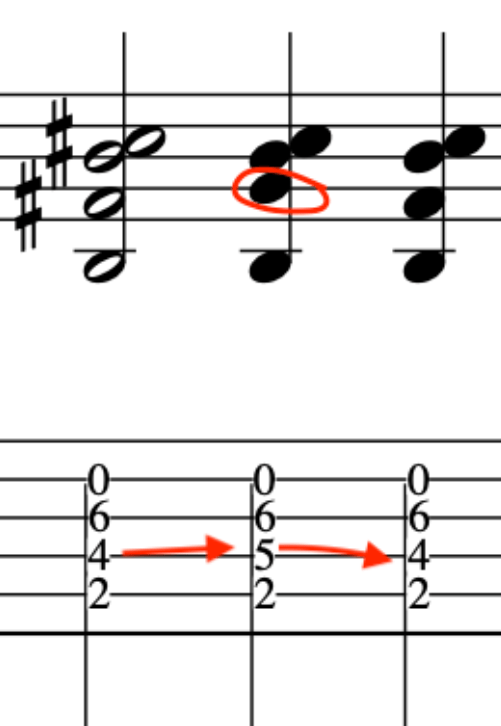
This time we will ascend and descend.
This exercise demonstrates the different amount of notes per string.
Many, alternate picking exercises revolve around the 3 notes per string concept.
But, real music dosen’t work that way as we have – Melodies/Vamps/Hooks/Riff/Unison Instruments-this means, there maybe 1 note on one string and 4 notes on the next string and then 2 notes on the next string and then 3 notes etc.
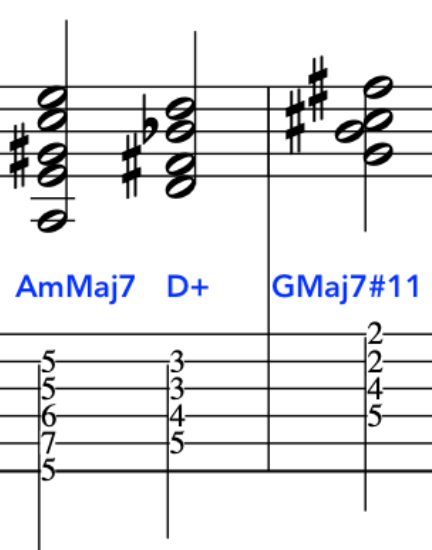
This exercise is tailor made for the above, as, it employs the two main music devices being that of an arpeggio and scale.
Here is the first part.
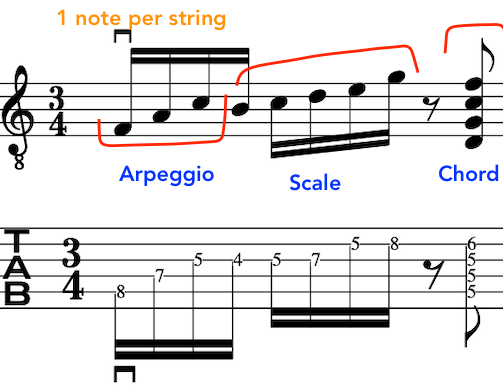
The second part, starts on an Upstroke, because, we finished the last phrase on a downstroke as we plucked the chord.
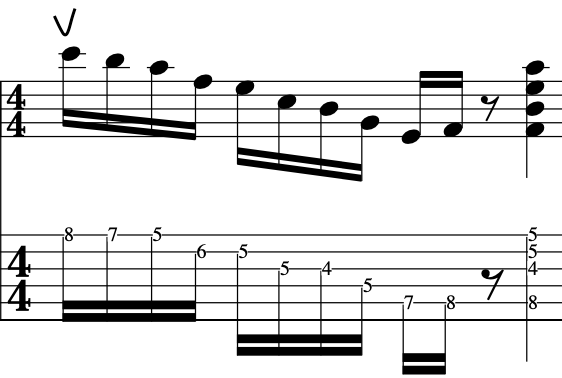
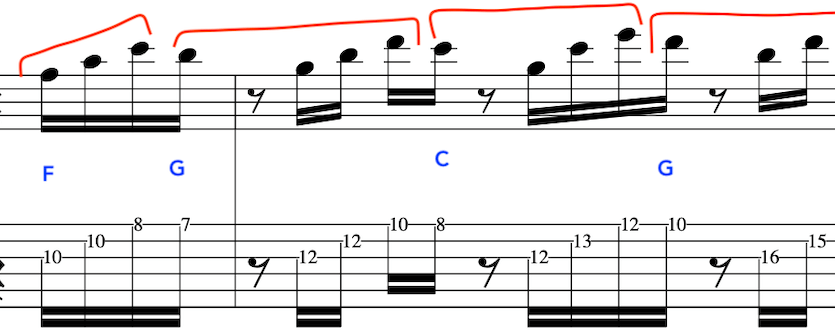
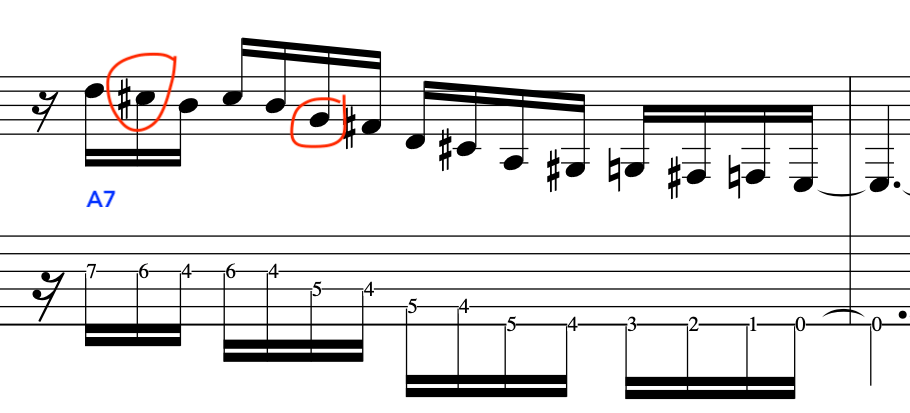
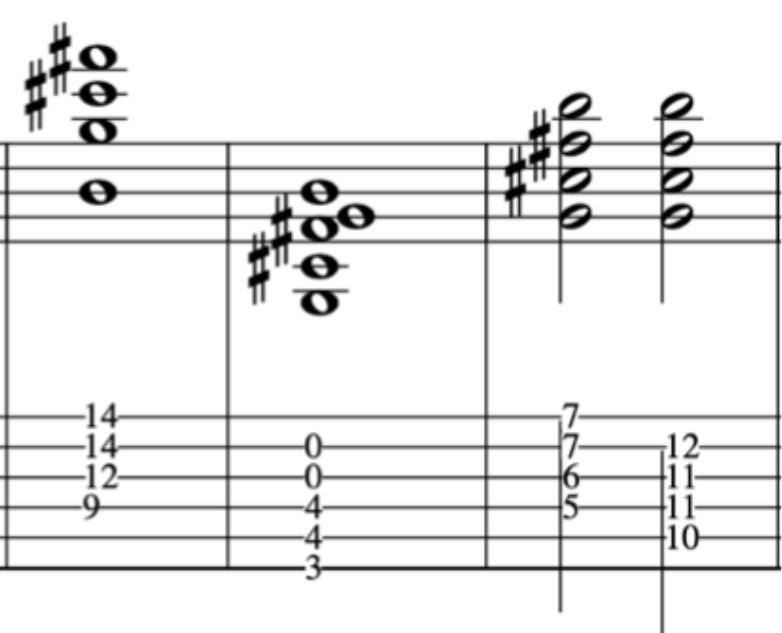
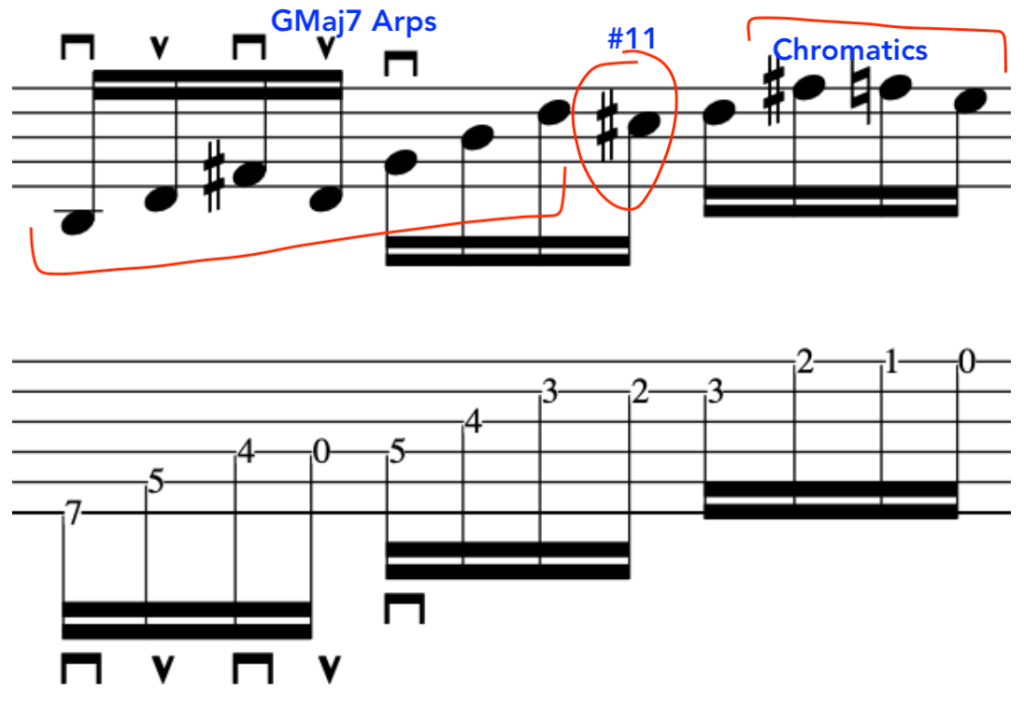
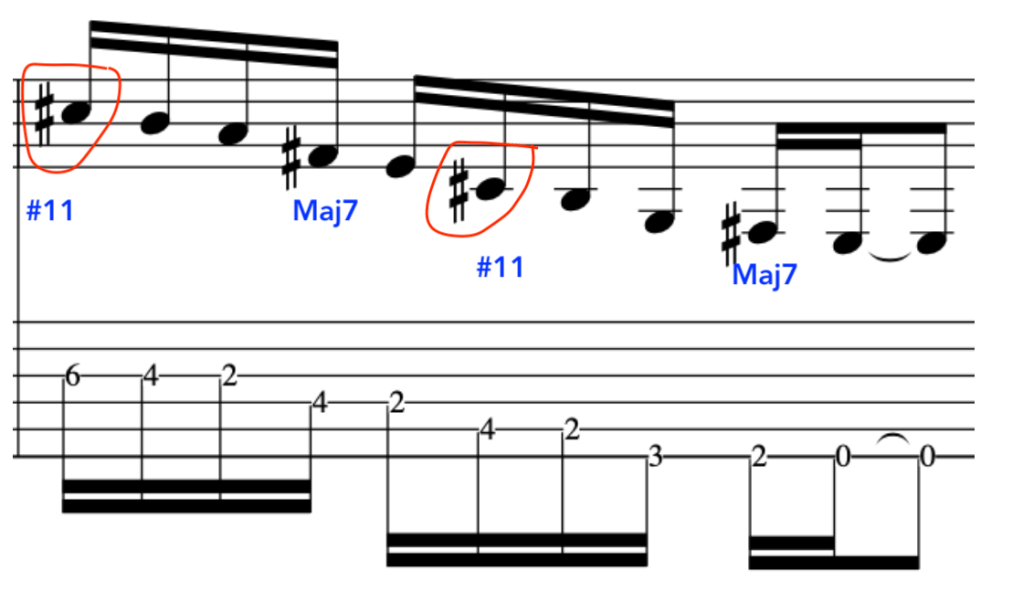
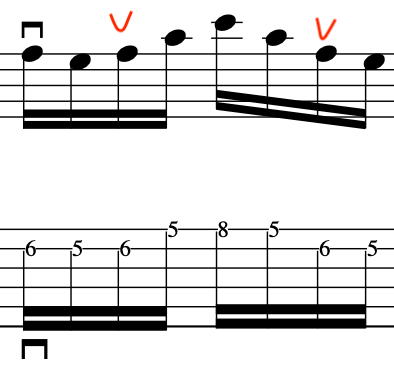
EXERCISE 4:
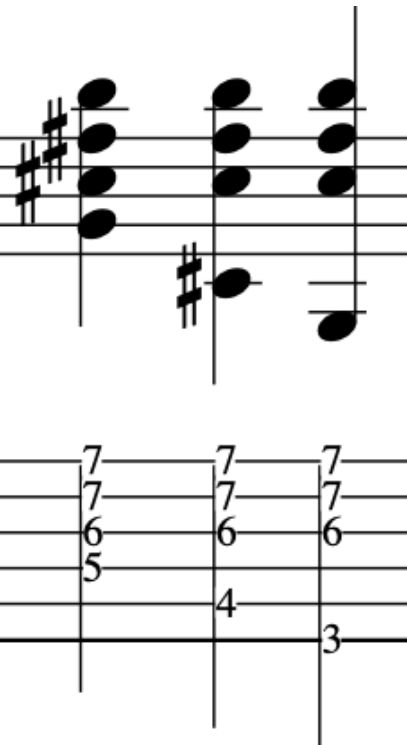
This exercise involves crossing over to the 1st string and back again, with different amounts per string.
So, to begin with let’s break this down into a simple 2 string exercise:
As before, notice the accents on the 3rd note in each 4 note grouping:
Full Exercise:
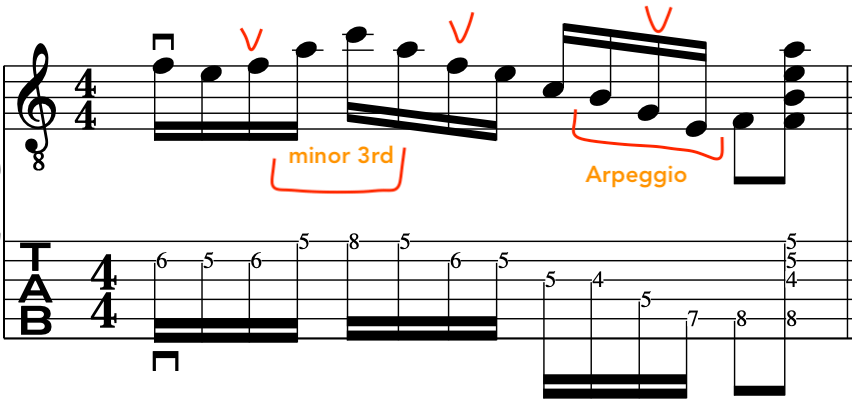
In conclusion:
These exercises are just a few ideas that are really useful when working on alternate picking guitar technique.
This is because many hooks and vamps and compositional devices don’t work on 3 note per string picking.
The great improvisers like John McLaughlin, Don Mock and Pat Martino play long fluid phrases along with weaving in and out of chords, chromaticism and implied harmony [double stops/Octaves]. So, being able to pluck odd and even groupings [or any amount of notes per string] with embellishments and chords is essential.
Hopefully, these exercises will be of some help with that.
PDF DOWNLOAD:
If this lesson was of use to you then please SUBSCRIBE to us on YOUTUBE below, Thanks!